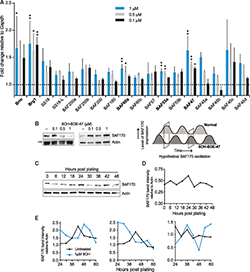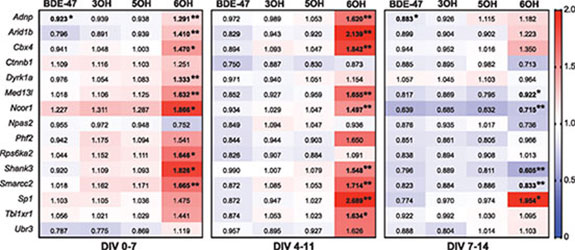
Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) are a pervasive class of brominated flame retardants that are present in the environment at particularly high levels, especially in the United States. Exposure to PBDEs has been strongly associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. However, the details of their mechanistic roles in such disorders are incompletely understood. Here, we report the effects of one of the most prevalent congeners, BDE-47, and its hydroxylated metabolites on the maturation and function of embryonic rat cortical neurons. Prolonged exposure to 6OH-BDE-47 produces the strongest effects amongst the parent BDE-47 congener and its tested hydroxylated metabolites. These effects include: i) disruption of transcriptional responses to neuronal activity, ii) dysregulation of multiple genes associated with neurodevelopmental disorders, and intriguingly, iii) altered expression of several subunits of the developmentally-relevant BAF chromatin remodeling complex, including the key subunit BAF170. Taken together, our data indicate that persistent exposure to 6OH-BDE-47 may interfere with neurodevelopmental chromatin remodeling mechanisms and gene transcription programs, which in turn are likely to interfere with downstream processes such as synapse development and overall functional maturity of neurons.
To read the entire article, please visit: https://academic.oup.com/eep/article/4/1/dvx020/4798935